Understanding Diagnosis Related Denials
We all understand the sinking feeling of a claim denial due to diagnosis errors. It’s a time-consuming hassle for your RCM team. Let’s tackle these denials head-on by understanding the most common issues and implementing some preventive measures for diagnosis related denials.
The Complexity of Diagnosis Related Denials
Diagnosis related denials can stem from various sources, including coding errors, insufficient documentation, and discrepancies between the diagnosis and the services provided. These denials often occur during the claims submission process, leading to delays in reimbursement and potential revenue loss for healthcare providers. Moreover, they can also impact patient care by creating administrative burdens and disrupting the care delivery process.
One of the primary reasons for diagnosis related denials is incomplete or inaccurate documentation. Healthcare providers must ensure that all diagnoses are clearly documented in the patient’s medical record, including supporting evidence such as test results, imaging studies, and physician notes. Failure to provide comprehensive documentation can result in denials or delays in reimbursement, as insurance companies may deem the services as medically unnecessary or not supported by the provided diagnosis.
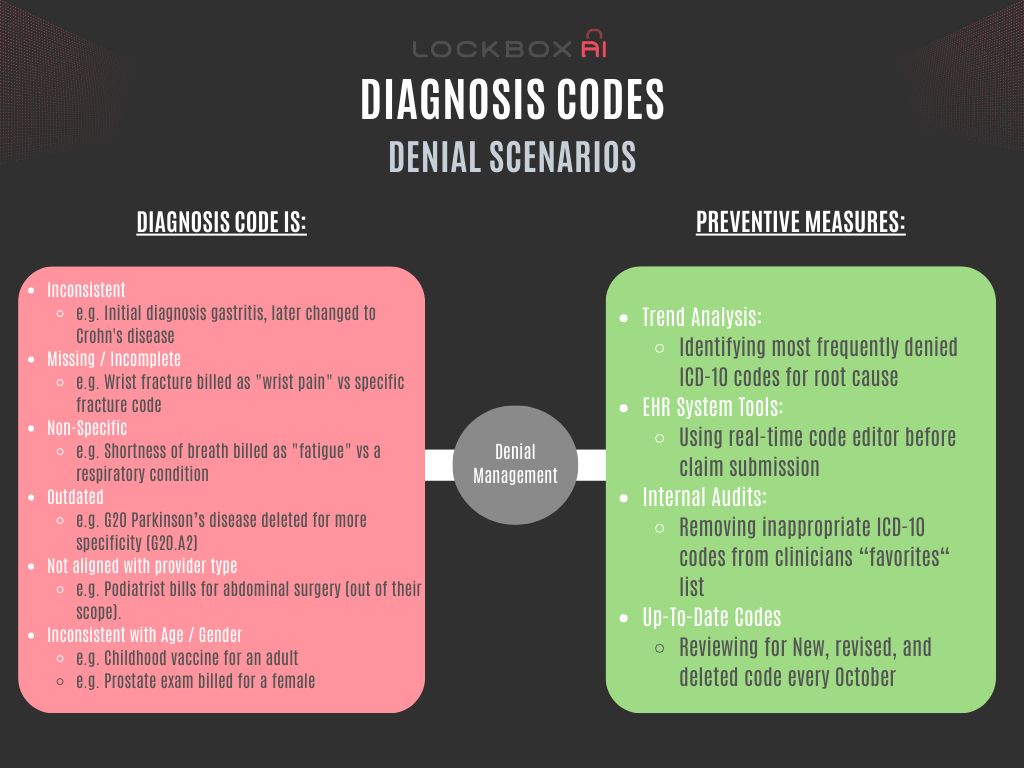
Top Diagnosis Related Denials Trigger:
- Inconsistent Diagnoses: This occurs when the diagnosis code(s) submitted don’t logically connect to the billed service or other listed diagnoses. Examples include:
- A claim for a sleep study with a diagnosis of a broken leg.
- A mammogram billed for a male patient.
- An appendectomy with a diagnosis of tonsillitis.
- Missing or Incomplete Diagnosis: If the diagnosis field is blank or lacks sufficient detail, the insurer won’t understand the medical necessity of the service.
- Diagnosis Codes Not Specific Enough: The code may not provide the necessary detail regarding the severity or nature of the condition. For example, using a generic code for “pain” without specifying the location or cause might lead to denial.
- Diagnosis Codes Incongruent with Patient Demographics:
- Age Discrepancy: A diagnosis of prostate cancer on a young child would raise red flags. Diagnosis codes should reflect conditions typically seen in a specific age group.
- Gender Incompatibility: Billing for a pregnancy test on a male patient is an obvious inconsistency. Diagnosis codes need to align with the patient’s biological sex.
- Diagnosis Codes Not Aligned with Provider Type: A dermatologist wouldn’t typically treat a heart condition. Diagnosis codes should reflect the provider’s specialty and expertise.
- Outdated ICD-10 Codes: Using an ICD-10 code no longer recognized by the insurance company results in a communication breakdown.
- Incorrect ICD-10 Codes: A typo or accidental selection of the wrong code can throw the entire claim into question.
The Role of DRGs and HCCs:
- DRGs (Diagnosis Related Groups): Used primarily for hospital reimbursement, DRGs classify patients based on diagnoses, procedures, and other factors. Accurate diagnosis coding is essential for correct DRG assignment, which directly impacts reimbursement.
- HCCs (Hierarchical Condition Categories): Medicare Advantage plans use HCCs to predict patient costs based on chronic conditions. Accurate diagnosis coding ensures appropriate risk scores for HCC assignment, leading to fair reimbursement for managing complex patients.
Preventing Diagnosis Denials:
- Trend Analysis in Reports: Regularly analyze denial reports to identify recurring diagnosis-related issues by the ICD-10 codes themselves. Pinpoint the patterns you see i.e. lack of specificity by the rendering provider. Remove vague or nonspecific codes from providers’ most-commonly-used list of choices.
- EHR System Tools: Utilize features like built-in coding assistance, real-time edits, and compliance checks within your Electronic Health Record (EHR) system to catch potential errors before claim submission.
- Clear Communication: Foster open communication between physicians and coders. Physicians should document diagnoses clearly and thoroughly, while coders can clarify any uncertainties before finalizing the claim.
- Ongoing Education: Invest in training for both coders and physicians on proper ICD-10 coding practices and common diagnosis-related denial triggers.
- Regular Audits: Conduct internal audits to proactively identify and address coding weakness and inconsistencies before claims are submitted.
- Stay up-to-date: ICD-10 codes are periodically revised, added and deleted. Keep up with the changes within your EHR system (even if the payors forget to do the same!).
Conclusion
Diagnosis related denials pose a significant challenge for healthcare organizations, impacting both financial performance and patient care quality. By implementing proactive denial management strategies and leveraging technology solutions, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of denials and optimize revenue capture. Moreover, fostering collaboration between providers, coding specialists, and payers is essential for addressing the root causes of denials and achieving long-term success in denial management. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, organizations must remain vigilant in their efforts to diagnose and resolve denial issues effectively.
Consider this short blog as a stepping stone on your journey to mastering avoidable coding denials. As healthcare evolves, so will the array of ICD 10 codes and coding requirements. Stay vigilant, curious, and keep learning. Remember, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of denial appeals.