Effective Strategies to Address Place of Service Denials
In the intricate world of medical billing, incorrect Place of Service (POS) coding remains a common cause of claim denials. Understanding POS codes, their significance, and the errors that lead to denials is crucial for streamlining the billing process and maximizing reimbursement.
The Role of POS Codes in Medical Billing
POS codes act as location tags for medical services, indicating to insurers where a service was provided, such as an office, hospital, or home. These codes play a significant role in determining reimbursement rates. Here are some common examples:
- 11: Office – Services provided in a physician’s office or group practice.
- 21: Inpatient Hospital – Services rendered during an overnight hospital stay.
- 22: Outpatient Hospital – Services provided in a hospital setting without an overnight stay.
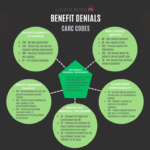
Common Scenarios Leading to Place of Service(POS) Code Denials
Claim denials related to missing, incorrect, or inconsistent POS codes can significantly impact revenue. Here are the most common scenarios:
- Missing POS Code: The absence of a POS code makes it impossible to determine where the service occurred, leading to denial.
- Invalid POS Code: A submitted code is either unrecognized or not applicable for the service provided.
- Inconsistent POS Code: The POS code does not align with other claim details, such as diagnosis or service codes.
- Mismatched Modifier and POS Code: The modifier used conflicts with the setting implied by the POS code.
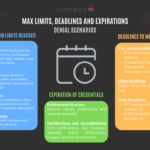
Denials Without a Rebill Option
Certain errors lead to denials that cannot be corrected by simply resubmitting the claim:
- Unbundling Due to Incorrect POS Code: Billing for individual components of a bundled service when the Place of Service (POS) code indicates bundled billing is required.
- Duplicate Billing with Conflicting POS Codes: Submitting the same service for payment under different POS codes.
- Fraudulent Activity: Misrepresenting the POS code to secure higher reimbursement, which can lead to serious consequences.
Telehealth Challenges and POS Coding
The rise of telehealth services has introduced additional complexity to POS coding. Accurate POS coding for telehealth is essential to avoid denials, but it requires specific training and awareness:
- Keeping Up with Code Changes: New POS codes for telehealth are frequently introduced or revised, requiring ongoing education for healthcare providers and billing staff.
- Understanding Location Requirements: Different Place of Service (POS) codes apply depending on where the patient is located during the telehealth visit. Accurate documentation is crucial for selecting the correct code.
- Documentation Challenges: Detailed documentation of the telehealth encounter is necessary to justify the chosen POS code.
Extended Flexibility for Telehealth Services
The Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023 has extended many telehealth waivers through December 31st, 2024, allowing for:
- Location Flexibility: Patients can receive telehealth services from any location within the U.S., removing previous geographic restrictions.
- Expanded Provider Eligibility: All Medicare-eligible healthcare providers, including Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs) and Rural Health Clinics (RHCs), can now offer telehealth services.
Leveraging Awareness and Proactive Solutions
While there is no one-size-fits-all solution to resolving missing POS code issues, raising awareness and implementing proactive measures can significantly reduce errors:
- Certification and Training: Encourage coders to maintain relevant certifications (CPC, CCS) that require ongoing education, ensuring they stay updated on coding guidelines.
- Internal Training Programs: Develop or participate in programs focused on the latest telehealth billing and coding updates, particularly for POS documentation.
- Industry Resources and Webinars: Utilize resources from coding associations (AAHCP, AAPC) that offer webinars and articles on current guidelines and best practices, with an emphasis on accurate POS capture.
- Coding Audits: Conduct regular coding audits with a focus on identifying missing or incorrect POS documentation, and provide constructive feedback to address areas needing improvement.
- Team Communication: Foster open communication between coders and clinicians to ensure complete documentation, particularly regarding POS information.
Proactive Documentation Solutions
Incorporating a strategically placed, pre-populated field for POS in progress note templates can be a simple yet effective strategy. If your system allows, making this field mandatory can further ensure that clinicians consistently include this critical detail. This small adjustment can lead to smoother billing processes, better revenue cycle management, and reduced time spent correcting missing information.
Conclusion
Clear communication and thorough documentation are the cornerstones of efficient healthcare delivery. By prioritizing awareness and implementing structured processes for POS documentation, healthcare facilities can minimize errors, streamline billing operations, and enhance overall revenue management. The key to success lies in combining education, proactive measures, and effective communication to ensure that the correct POS codes are consistently used.